Exhaust Gas Boiler System as a Waste Heat Recovery System
1:- Overview of Exhaust Gas Boiler
Exhaust Gas Boilers (EGB) and Waste Heat Recovery Systems (WHRS) are essential for improving energy efficiency by utilizing the heat from engine exhaust gases and reducing fuel consumption to generate steam from the boiler.
2:- What is a Waste Heat Recovery System?
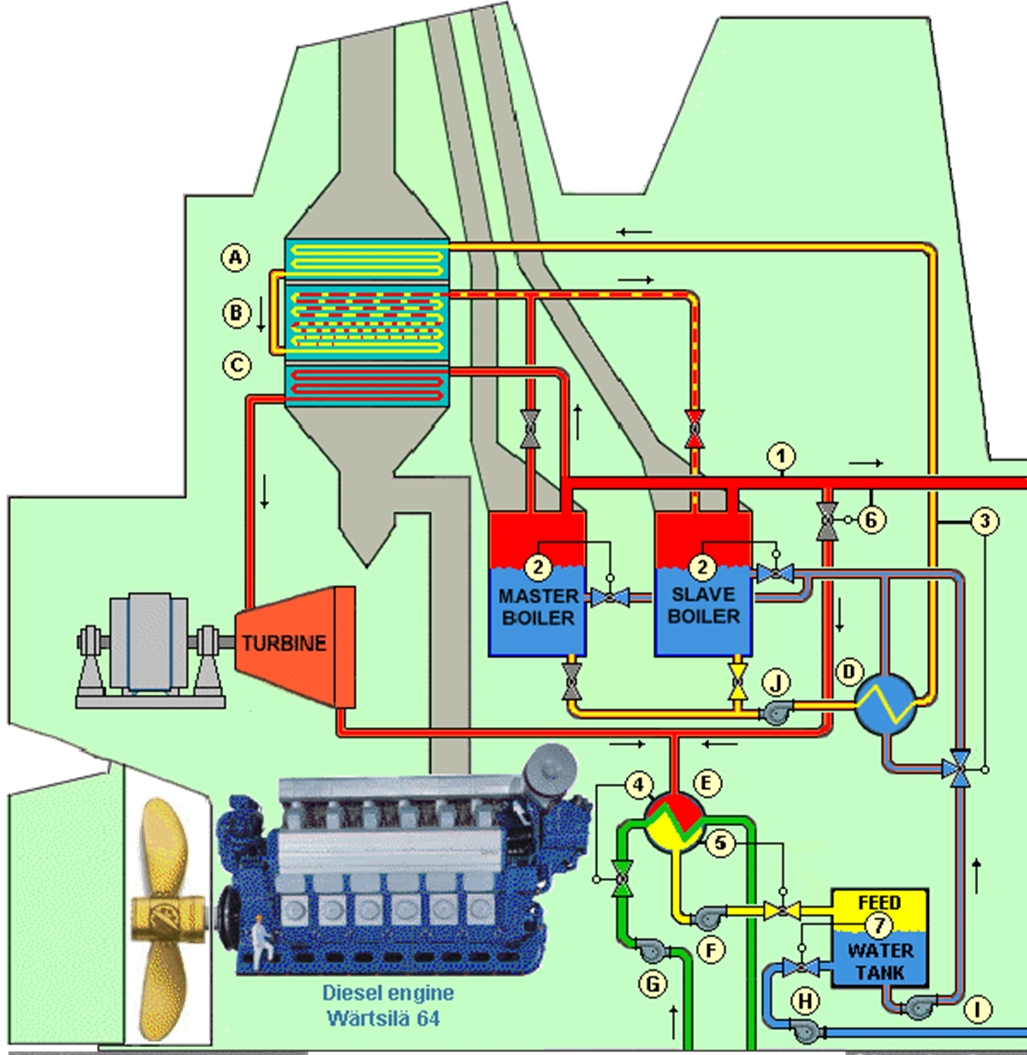
A Waste Heat Recovery System (WHRS) captures the waste heat from the exhaust gases of diesel engines of ships (main engine) and uses it to generate electrical energy and steam for ship services.
This system significantly improves energy efficiency, reduces fuel consumption, and minimizes environmental impacts such as pollution.
Key Components of Waste Heat Recovery Systems:
- Economizer: Preheats water before it enters the evaporator.
- Evaporator: Converts water into steam.
- Superheater: Further heats the steam to super saturated form before it is used by the turbine.
- Condenser: Converts exhaust steam back into water (Condensate).
2.1:- What is the Main Function of a Waste Heat Recovery System?
Waste heat recovery systems recover the thermal energy from the exhaust gas of the ship’s engine and convert it into electrical energy, while the residual heat can further be used for ship services (such as hot water and steam) through heat exchangers.
2.2:- What is the Role of the Exhaust Gas System and Waste Heat Recovery System in an Economizer?
In the economizer, the hot exhaust gases pass over a series of tubes containing water. The heat from the gases raises the temperature of the water, reducing the amount of fuel required by oil-fired boilers or other ship systems to generate steam. This process significantly improves energy efficiency by utilizing waste heat that would otherwise be lost.
The exhaust gas system channels hot gases produced by the main engine out of the ship. Instead of releasing this heat directly into the atmosphere, the system directs these gases through an economizer, which is a type of heat exchanger.
Want to learn more about Boiler, why don’t you check out our Boiler System package to get an in-depth knowledge about the Boiler system and maintenance onboard ship?
3:- What is an Exhaust Gas Boiler (EGB)
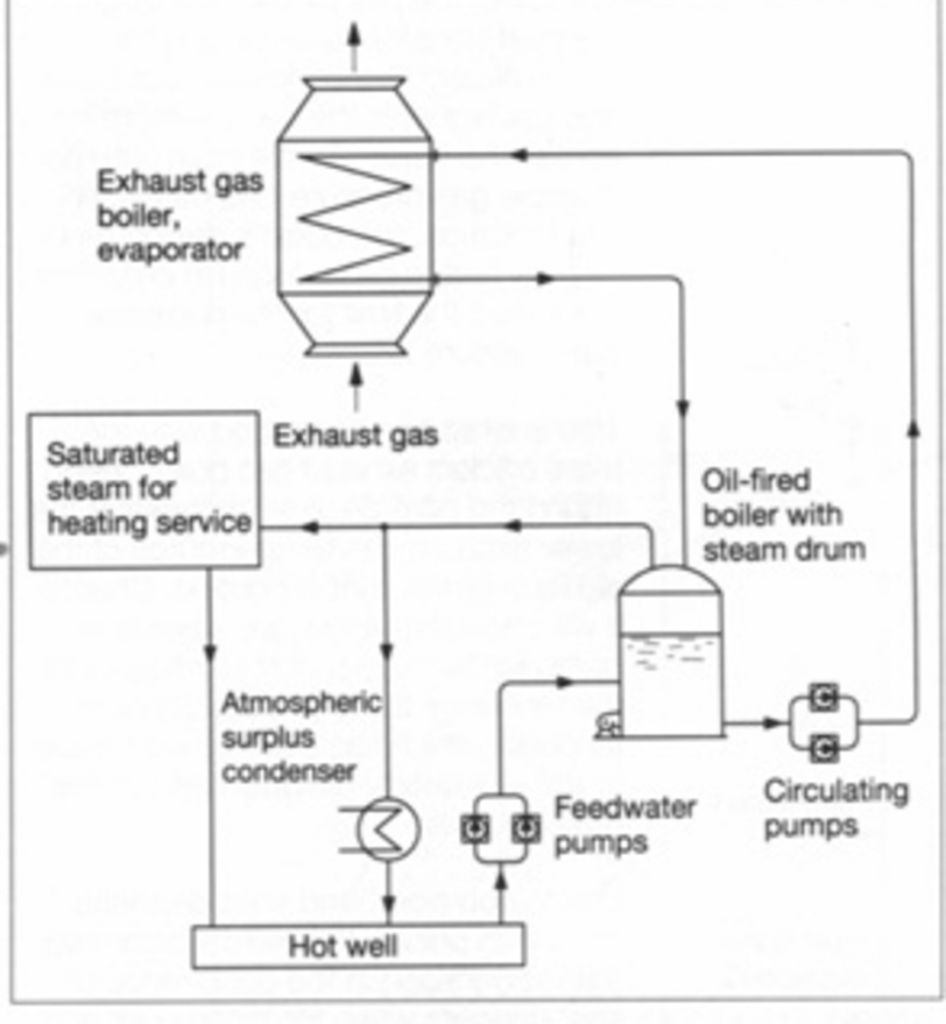
An Exhaust Gas Boiler (EGB), also known as an Exhaust Gas Economizer, is a device that recovers heat from the exhaust gases of a ship’s engine. The recovered heat from the exhaust gases is used to produce steam, which can then be utilized for various ship operations.
3.1:- Why is an Exhaust Gas Boiler Important?
A diesel engine loses about 30% of its energy to exhaust gases. Turbochargers recover some of this energy, but significant heat remains that can be recovered using an Exhaust Gas Boiler. The efficiency of the Exhaust Gas Boiler ensures that energy losses are minimized, which leads to fuel savings.
3.2:- What is the Ideal Steam Production in Exhaust Gas Boilers?
Exhaust Gas Boiler used without an additional economizer, the best steam production is usually at a pressure of 3-4 bar, with a steam temperature of 143-151°C. To maintain efficiency, the temperature difference between the exhaust gas and steam (called the pinch temperature) should be at least 25°C.
3.3:- Why is Tube Design Important in Exhaust Gas Boilers?
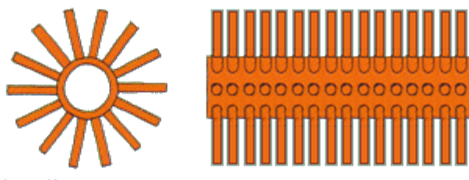
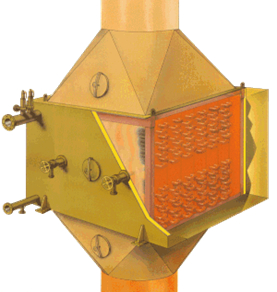
In Exhaust gas boiler tubes with extended surfaces help capture more heat from the exhaust gases, making the boiler more efficient. Pinned or finned tubes increase the surface area for heat transfer, allowing the Exhaust Gas Boiler to extract as much energy as possible.
3.4:- How Can Soot Affect an Exhaust Gas Boiler?
Soot from exhaust gases can build up inside the boiler, reducing steam production and efficiency. If soot is left to accumulate, it can cause a fire. To prevent this, an automatic soot-blowing system is often used to clean the tubes regularly.
4:- Steam Generation and Uses of Steam on Ship
Steam is used on ships for heating, ships often use saturated steam at around 6.0 kg/cm², which is distributed to different parts of the vessel through a common pipeline.
However, for more complex applications like propulsion or electricity generation using steam turbines, the steam needs to be superheated and maintained at a higher pressure.
Steam generation requires larger, more sophisticated systems, including bigger boilers, exhaust gas economizers, and condensers.
4.1:- Common Uses of Steam on Ships
Steam is widely used on vessels for various uses, such as:
1. As a working medium for driving steam turbines where steam turbines are used for propulsion.
2. For turbo generators on steam and diesel engine vessels
3. For heating of fuel oil (of high viscosity) in tanks to reduce viscosity.
4. For geysers in accommodation spaces (for domestic use).
5. For air conditioning system for purpose of heating.(AHU)
6. For heaters of purifiers and fuel oil service system.
7. For heating crude oil or products in crude or product carriers
8. For windlass and mooring winches (Deck Machinery)
If you want to know why we use boilers on ship, here is the blog by Merchant Navy Decoded What is Boiler ? Why do we use boiler on ship?
5:- Why Heat Exchangers are Used in Waste Heat Recovery Systems?
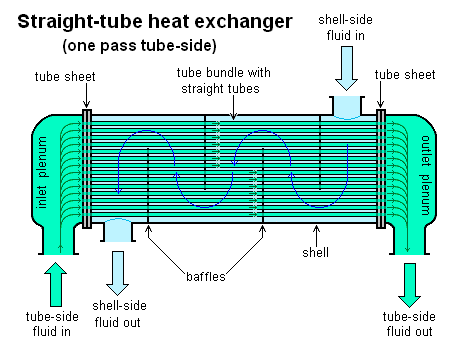
Heat exchangers are essential components on ships, used to transfer heat between liquids and gases in waste heat recovery systems on ships, improving energy efficiency and reducing fuel consumption.
This process is crucial for various onboard systems, such as heating fuel, lubricating oil, and water through heat exchangers. When the ship’s engine isn’t running, an auxiliary boiler, powered by liquid fuel is used to generate the heat in the form of steam.
There are different types of heat exchangers used on ships, including:
- Plate Heat Exchangers: Thin plates transfer heat between liquids, maximizing surface area for efficient heat transfer.
- Tube Heat Exchangers: These use tubes to pass fluids through, allowing heat to transfer effectively between them.
6:- Role of Turbocharger in Waste Heat Recovery System (WHRS)
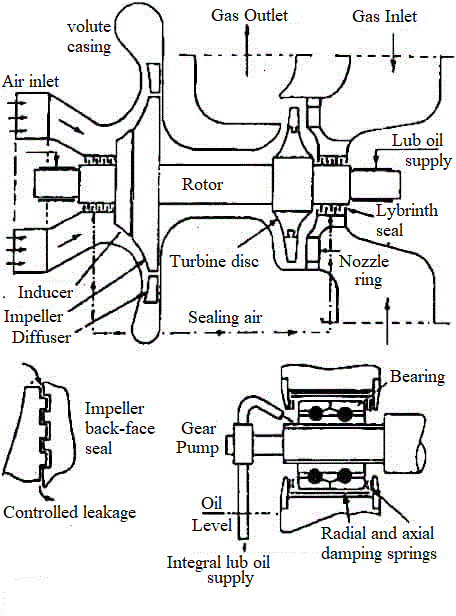
The turbocharger in a Waste Heat Recovery System (WHRS) helps boost engine efficiency by using exhaust gases to compress air for better combustion in the combustion chamber. After powering the turbocharger, the hot exhaust gases still contain energy, which is captured by the Waste Heat Recovery System to produce steam for various purpose onboard ship.
If want to know more about the turbocharger ships, refer to the detailed blog by Merchant Navy Decoded: turbocharger
7:- Conclusion
Exhaust gas boilers (EGB) and waste heat recovery systems (WHRS) use exhaust gases to generate steam for ship operations, which increases energy efficiency.
Heat exchangers are essential for transferring heat between fluids, which improves ship performance and fuel efficiency.
Disclaimer :- The opinions expressed in this article belong solely to the author and may not necessarily reflect those of Merchant Navy Decoded. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information provided and disclaim any responsibility for it. Data and visuals used are sourced from publicly available information and may not be authenticated by any regulatory body. Reviews and comments appearing on our blogs represent the opinions of individuals and do not necessarily reflect the views of Merchant Navy Decoded. We are not responsible for any loss or damage resulting from reliance on these reviews or comments.
Reproduction, copying, sharing, or use of the article or images in any form is strictly prohibited without prior permission from both the author and Merchant Navy Decoded.