IMDG Code and Categories of IMDG Code
1:- What Is the IMDG Code?
The IMDG Code is like a rulebook for shipping dangerous goods by sea. It ensures that ships follow safety guidelines to prevent accidents and pollution.
2:- History of the IMDG Code
The IMDG Code, or International Maritime Dangerous Goods Code, was created in 1965 as a set of recommendations for safely transporting dangerous goods by sea. In 2002, it became mandatory under the SOLAS (Safety of Life at Sea) Convention, and from January 1, 2004, all ships had to follow its guidelines. The Code is regularly updated every two years to improve safety and prevent pollution.
3:- What’s Inside the IMDG Code?
The IMDG Code covers several important areas:
- Packing: Securely packaging dangerous goods, similar to wrapping fragile items.
- Container Traffic: Guidelines for shipping containerized goods.
- Stowage: Instructions on where to place goods on the ship, like organizing your luggage.
- Segregation: Keeping incompatible substances apart to avoid reactions.
- Emergency Preparedness: Ways to handle emergencies involving dangerous goods.
4:- IMDG Code Contents
4.1:- Applicability of IMDG Code
The IMDG Code applies to all dangerous goods transported by sea, whether on large cargo ships or smaller vessels. This includes explosive substances, flammable gases, corrosive materials, and other hazardous items.
If you want to learn more about the IMDG Code and more such codes and authorities in the Merchant Navy then check out our MEO Class 4 package which will help you clear MEO Class 4 easily.
4.2:- Categories Covered in IMDG Code
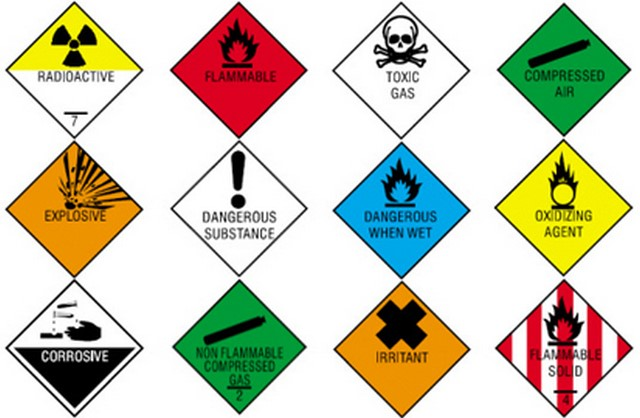

The IMDG Code covers a wide range of hazardous materials, such as:
- Explosive Substances: Dynamite, fireworks, ammunition.
- Flammable Gases: Easily ignitable gases.
- Flammable Liquids: Gasoline, alcohol.
- Flammable Solids: Materials that can catch fire.
- Oxidizing Substances and Organic Peroxides: Enhance combustion.
- Toxic and Infectious Substances: Harmful to health.
- Radioactive Materials: Emit radiation.
- Corrosive Substances: Substances that can damage other materials.
- Miscellaneous Hazardous Substances: Other dangerous goods.
4.3:- Safety Measures in IMDG Code
The IMDG Code sets strict rules for:
- Classification: Categorizing goods based on their properties.
- Labeling: Marking containers with hazard symbols.
- Packaging: Safe packing to prevent leaks or spills.
- Stowage: Proper placement on the ship.
- Handling: Guidelines for crew members.
- Transport: Safe movement of these goods.
5:- IMDG Code Class
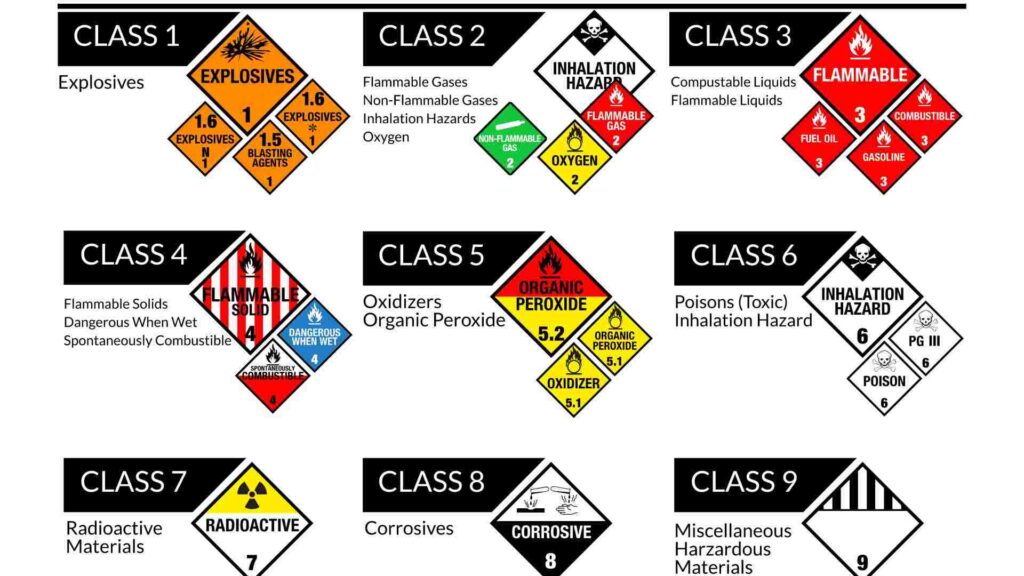
The IMDG Code classifies dangerous goods into nine main classes, each with specific characteristics and hazards:
5.1:- IMDG Code Class 1: Explosives

IMDG Code Class 1 covers explosive substances and articles that pose significant risks due to their potential for rapid combustion or detonation. This class includes items like fireworks, ammunition, and certain chemicals that are prone to explode. The IMDG Code mandates stringent regulations for handling, packaging, and transporting these materials to ensure safety and prevent accidental explosions.
- Examples: Dynamite, fireworks, ammunition.
- Hazards: Explosions, fires, fragment projections.
5.2:- IMDG Code Class 2: Gases

Class 2 of the IMDG Code includes gases that are compressed, liquefied, or dissolved under pressure. These can be flammable, non-flammable, or toxic gases such as propane, oxygen, and chlorine. The IMDG Code specifies safety measures for the storage, handling, and transport of gases to prevent leaks, explosions, and health hazards.
- Examples:
- Flammable Gases: Propane, butane.
- Toxic Gases: Chlorine, ammonia.
- Corrosive Gases: Hydrogen chloride.
- Hazards: Fire, toxicity, material damage.
5.3:- IMDG Code Class 3: Flammable Liquids

IMDG Code Class 3 includes flammable liquids that can ignite easily at normal temperatures. Examples include gasoline, alcohol, and acetone. The IMDG Code outlines strict guidelines for the packaging, labeling, and transport of these liquids to minimize fire risks during transportation.
- Examples: Gasoline, alcohol, diesel.
- Hazards: Fire.
5.4:- IMDG Code Class 4: Flammable Solids
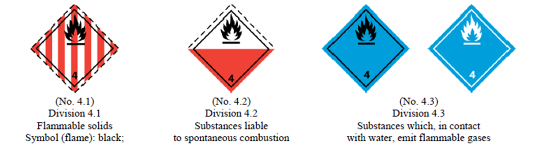
IMDG Code Class 4 covers flammable solids, substances liable to spontaneous combustion, and materials that emit flammable gases when in contact with water. Examples include matches, sulfur, and certain metal powders. The IMDG Code requires careful handling and specific packaging to prevent ignition and ensure safe transport.
- Examples: Matches, sulfur, and other metals.
- Hazards: Fire, heat generation.
5.5:- IMDG Code Class 5: Oxidizing Substances and Organic Peroxides

IMDG Class 5 includes oxidizing substances, which can cause or intensify fires, and organic peroxides, which can be explosive and highly reactive. Common examples are hydrogen peroxide and potassium nitrate. The IMDG Code prescribes detailed safety protocols for the transport and storage of these reactive materials.
- Examples: Hydrogen peroxide, and potassium permanganate.
- Hazards: Fire, explosions, reactivity with other materials.
5.6:- IMDG Code Class 6: Toxic and Infectious Substances

IMDG Code Class 6 covers toxic substances that can cause serious health risks and infectious substances containing pathogens. Examples include pesticides, arsenic compounds, and medical waste. The IMDG Code enforces stringent regulations to ensure these substances are transported safely, with minimal risk to human health and the environment.
- Examples: Pesticides, medical waste, and infectious materials.
- Hazards: Health risks, contamination.
5.7:- IMDG Code Class 7: Radioactive Materials

IMDG Code Class 7 includes radioactive materials that emit ionizing radiation, which can be harmful to living organisms. Examples are uranium, plutonium, and medical isotopes. The IMDG Code requires rigorous safety measures, including specialized packaging and labeling, to protect against radiation exposure during transportation.
- Examples: Uranium, and plutonium.
- Hazards: Radiation exposure.
5.8:- IMDG Code Class 8: Corrosive Substances

IMDG Class 8 covers corrosive substances that can cause severe damage to living tissue and other materials. Examples include sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, and caustic soda. The IMDG Code mandates specific handling, packaging, and transportation guidelines to prevent leaks and ensure safety.
- Examples: Sulfuric acid, and sodium hydroxide.
- Hazards: Burns, corrosion.
5.9:- IMDG Code Class 9: Miscellaneous Hazardous Substances

IMDG Class 9 includes a variety of hazardous materials that do not fall into the other classes but still pose significant risks. This class encompasses substances like asbestos, dry ice, and lithium batteries. The IMDG Code provides comprehensive guidelines to ensure the safe transport of these diverse materials, addressing their unique hazards.
- Examples: Lithium batteries, asbestos.
- Hazards: Vary based on the specific substance.
The IMDG Code is essential for the safe transportation of dangerous goods by sea, helping to protect people, ships, and the environment.
6:- Importance of the IMDG Code

The IMDG Code plays a crucial role in maritime safety and environmental protection. By providing comprehensive guidelines for the classification, packaging, labeling, stowage, and handling of dangerous goods, the IMDG Code helps prevent accidents and incidents at sea. This ensures the safety of the crew, the ship, and the environment. Additionally, the Code facilitates international trade by standardizing the regulations across different countries, making it easier for shipping companies to comply with safety requirements globally. The IMDG Code’s regular updates ensure that it keeps pace with new scientific and technical developments, continually enhancing its effectiveness in managing the risks associated with transporting hazardous materials.
7:- Conclusion
The IMDG Code is an essential framework for ensuring the safe and efficient transport of dangerous goods by sea. Its comprehensive guidelines help prevent accidents, protect the environment, and facilitate international trade. By adhering to the IMDG Code, shipping companies can significantly reduce the risks associated with hazardous materials, safeguarding lives and preserving marine ecosystems. The ongoing evolution of the IMDG Code underscores its importance in adapting to new challenges and maintaining high safety standards in the maritime industry.
Disclaimer :- The opinions expressed in this article belong solely to the author and may not necessarily reflect those of Merchant Navy Decoded. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information provided and disclaim any responsibility for it. Data and visuals used are sourced from publicly available information and may not be authenticated by any regulatory body. Reviews and comments appearing on our blogs represent the opinions of individuals and do not necessarily reflect the views of Merchant Navy Decoded. We are not responsible for any loss or damage resulting from reliance on these reviews or comments.
Reproduction, copying, sharing, or use of the article or images in any form is strictly prohibited without prior permission from both the author and Merchant Navy Decoded.




