Digitalization in Shipping Industry
Table of contents
1. Overview
Digitalization is the process of using digital technologies to revolutionize traditional corporate processes and operations, it comprises the integration of technologies such as IoT, AI, Big Data Analytics, and Blockchain to improve efficiency, safety, and sustainability.
It also includes digitizing data and processes, allowing for real-time monitoring, analysis, and decision-making.
Digitalization in the maritime industry makes it easier to connect vessels, ports, and shore-based activities, enhancing communication and collaboration. Digitization aims to streamline operations, cut costs, and boost the maritime industry’s competitiveness and sustainability.
Digitalization, digitization, and digital transformation are sometimes used interchangeably, although they have different significance in the context of the advancement of technology and business growth.
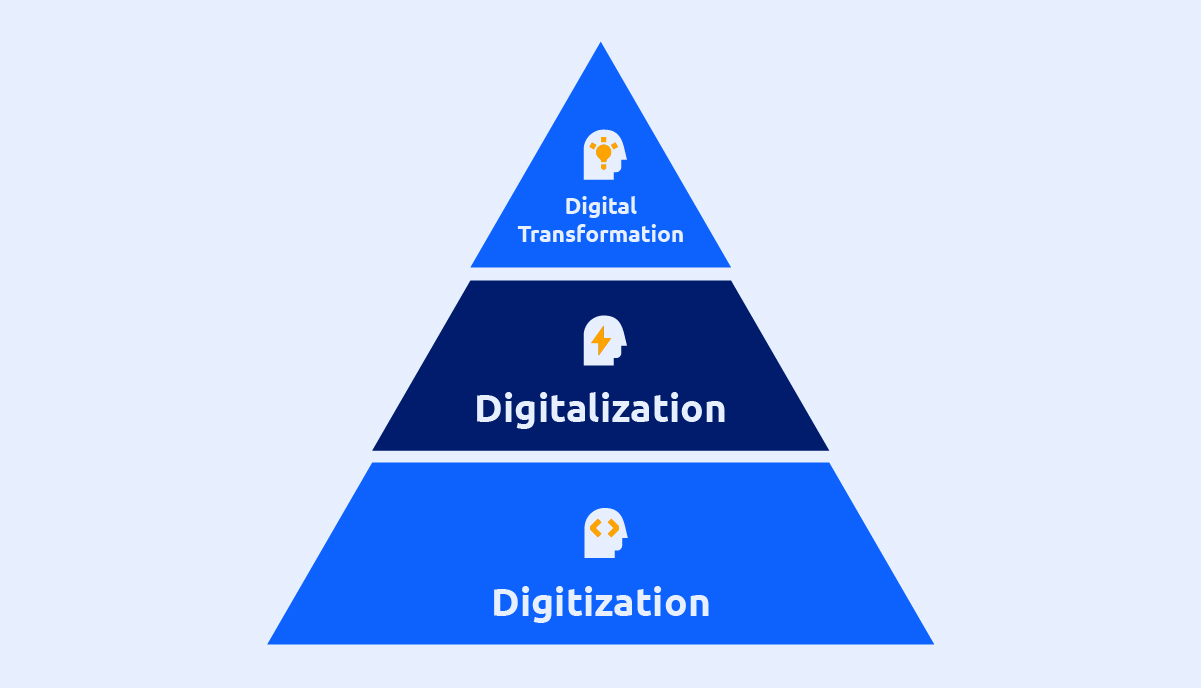
1.1 What is Digitization?
Digitization is the process of transforming information from a physical format to a digital one. This entails scanning, recording, or otherwise collecting analog data in digital form.
Example:
Examples of digitization include the conversion of paper documents into electronic data and music from CDs to MP3 files.
Benefits of Digitization:
Digitization is the process of transforming analog data into a digital version that can be stored, accessed, and processed more easily.
1.2 What is Digitalization?
The term “digitalization” refers to a more general process of utilizing digital technologies to revolutionize corporate procedures and develop new business strategies. It extends beyond just transforming analog data to digital format.
Example:
For example, in the marine industry, digitalization might involve installing IoT sensors on ships to monitor engine performance in real-time, allowing for predictive maintenance and decreasing downtime.
1.3 What is Digital Transformation?
Digital transformation is the highest of the three phases. It refers to transforming corporate processes and models using digital technologies.
Digital transformation is more than just using technology to perform the same tasks more efficiently; it is about radically altering how a company runs and provides value to its customers.
This could include entirely new methods of operation, new revenue streams, and even new business models. The necessity to remain competitive in a fast-changing digital world frequently drives digital transformation.
| Aspect | Digitization | Digitalization | Digital Transformation |
| Definition | Converting analog data to digital format. | Using digital technologies to improve processes and create new business models. | Completely changing business processes and models using digital technologies. |
| Example | Scanning paper documents to create digital copies. | Using IoT sensors on ships for real-time monitoring. | Implementing AI for predictive analytics and automation. |
| Focus | Data conversion. | Process improvement and new business models. | Fundamental business change. |
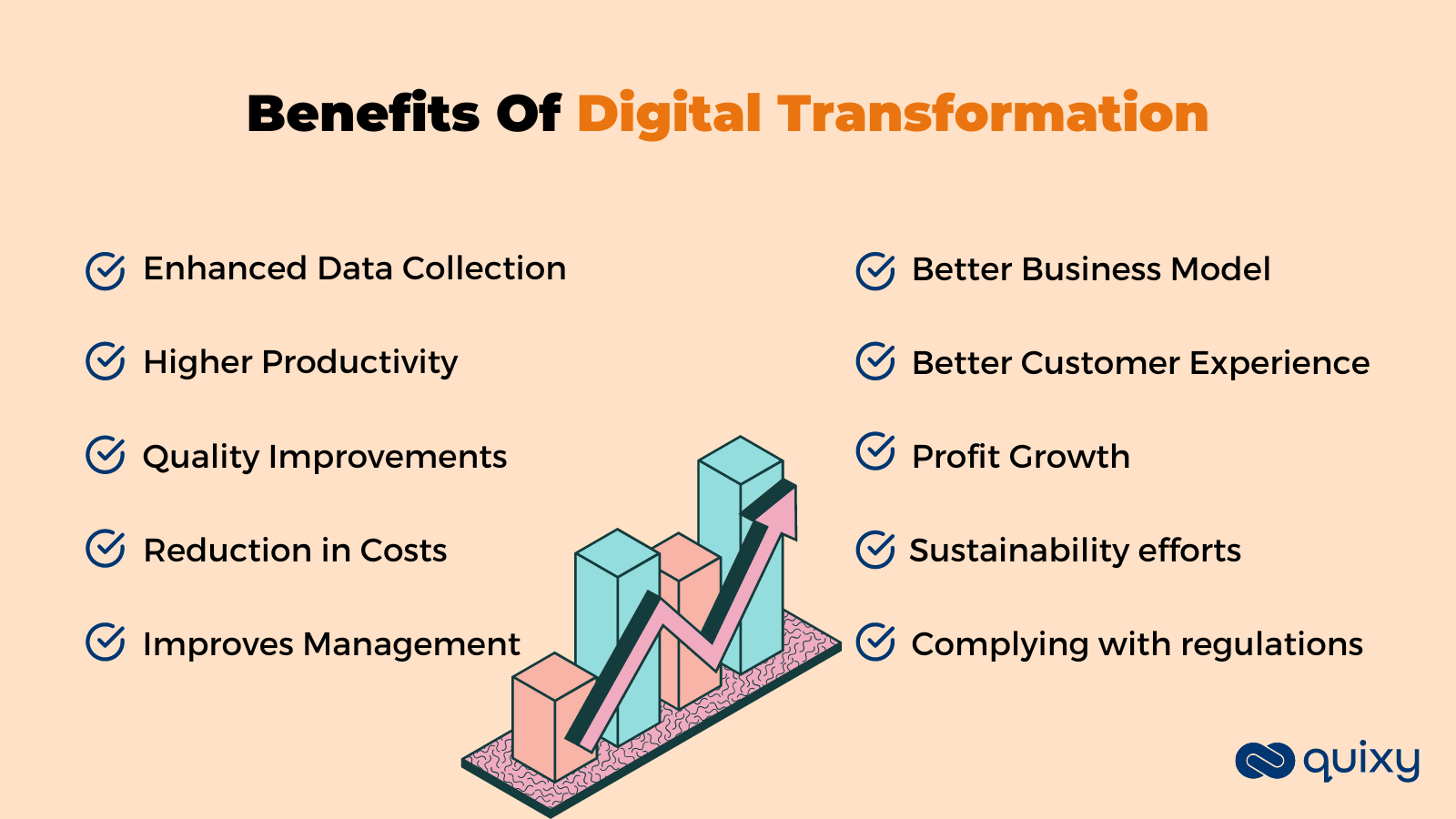
2. Benefits of Digital Transformation
3. What is Digital Implementation?
Digital implementation means integrating digital technologies into an organization’s activities to increase efficiency and effectiveness. It involves installing digital technologies, educating staff, incorporating them into workflows, and tracking their effectiveness.
How is digital implementation different from digitization, digitalization, and digital transformation?
Digital implementation focuses on the practical aspects of implementing digital technologies within an organization. It comprises the actual implementation, integration, and administration of digital tools and systems to fulfill specific corporate goals.
4. What is Maritime Digitalization?
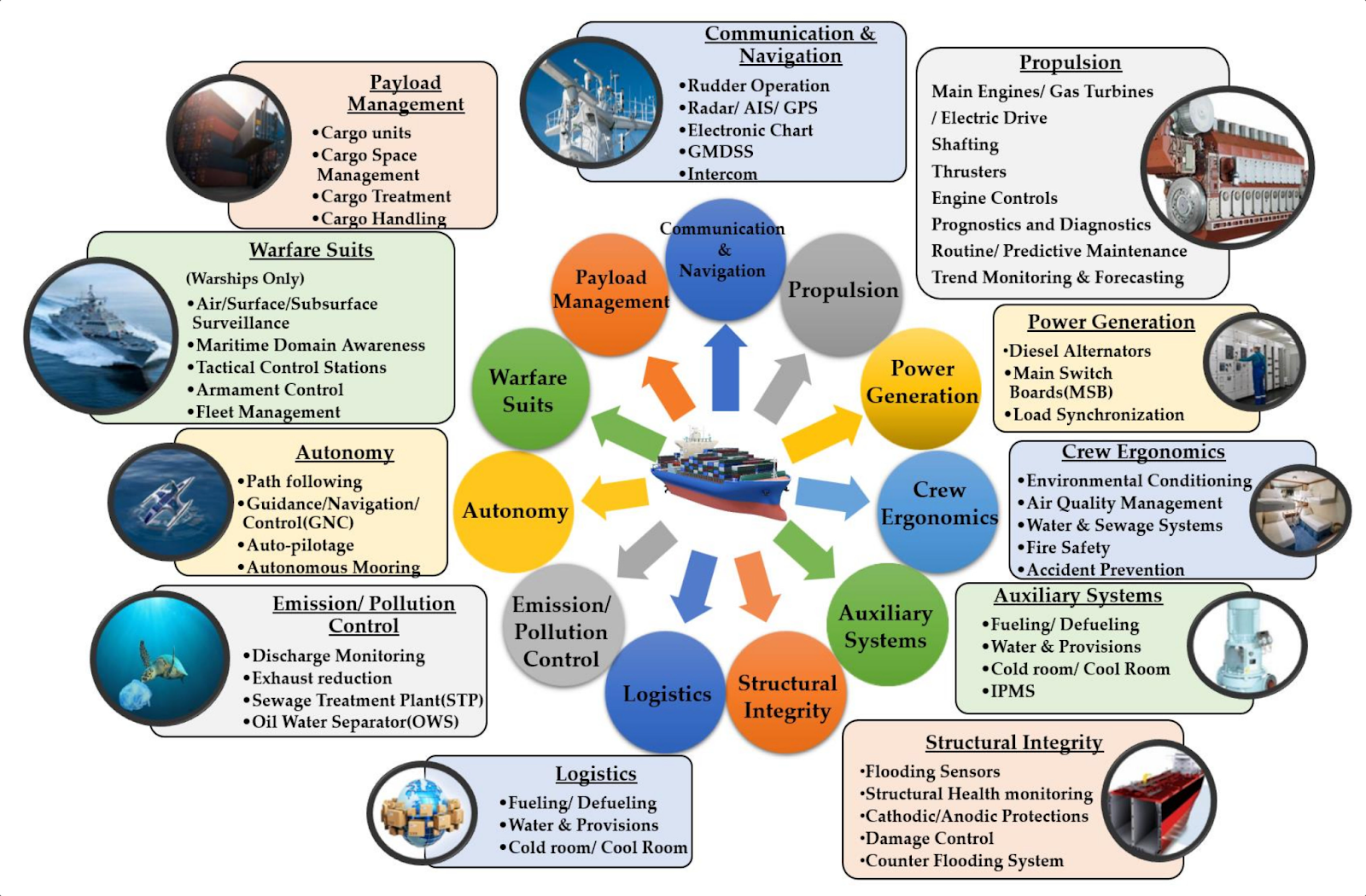
Marine digitalization is the application of digital technologies in the marine industry to increase efficiency, safety, and sustainability.
IoT, AI, Big Data Analytics, and Blockchain technologies are being integrated into different parts of maritime operations, such as vessel management, navigation, cargo handling, and port operations.
Maritime Digitalization also improves connectivity between ships, ports, and shore-based operations, resulting in increased collaboration and communication in the marine industry.
Enroll in our package, crafted by the best in this field. Maritime Digitalization
5. Digitalization in Maritime Industry

Maritime digitization in the merchant navy and maritime sector is currently progressing through several critical stages, with each structure improving on the previous one to improve efficiency, safety, and sustainability:
- Ship Electrification and Digitization: The first stage was to electrify ships and digitize their machinery. This involved switching from old mechanical and analog systems to digital and electrical ones, like electric propulsion, digital engine controls, and integrated bridge systems.
- Digitalization: As ships became more computerized, the emphasis switched to using data from onboard systems to improve decision-making. This phase includes implementing data analytics, predictive maintenance, and remote monitoring to improve vessel performance and reduce downtime.
- Smart Ship: The concept of the smart ship evolved as digitization progressed. Smart ships are outfitted with modern sensors, communication solutions, and automation systems that allow for real-time data collection, analysis, and decision-making. This technology enables more efficient operations, increased safety, and better environmental performance.
- Autonomous Marine Vehicles: The most recent advance in maritime digitalization is the development of autonomous marine vehicles (AMVs). These include unmanned surface vessels, underwater drones, and autonomous ships.
AMVs are equipped with AI, advanced sensors, and communication systems, allowing them to function autonomously or with minimum human interaction. They have the potential to increase productivity, save costs, and improve safety in maritime operations.
6. Case Study of Wärtsilä and Rolls-Royce

Wärtsilä and Rolls-Royce are two premier naval companies and their successful testing and demonstration of a completely autonomous ferry for dock-to-dock navigation without human intervention is a significant advancement in autonomous shipping.

This result demonstrates autonomous technology’s potential to revolutionize the maritime sector by increasing efficiency, safety, and sustainability. Autonomous ferries and ships have the potential to transform transportation by lowering operational costs and minimizing environmental impact. It will be interesting to see how this technology advances and gets utilized in the next years.
7. Conclusion

In conclusion, digitalization is revolutionizing the maritime industry, increasing efficiency, safety, and sustainability. Digitization establishes a foundation by transforming analog data to digital, whereas digitalization incorporates digital technologies to improve processes and build new business models.
Maritime digitization is fast progressing, from ship electrification to the development of self-driving marine vehicles, transforming operations and increasing communication. The successful testing of autonomous ferries by Wärtsilä and Rolls-Royce demonstrates autonomous technology’s potential to change maritime transport.
Thank you for choosing Merchant Navy Decoded as your trusted platform!
8. FAQ
Q1: What are the key technologies driving digitalization in the maritime industry?
Ans. The key technologies driving digitalization in the maritime industry include IoT (Internet of Things), AI (Artificial Intelligence), Big Data Analytics, Machine learning, Deep Learning, Algorithms, and Blockchain. These technologies are being used to improve maritime operations’ efficiency, safety, and sustainability.
Q2: How is digitalization improving efficiency and safety in maritime operations?
Ans. Digitalization is improving efficiency and safety in maritime operations by enabling real-time monitoring, analysis, and decision-making. It allows for better communication and collaboration between ships, ports, and shore-based operations, leading to more efficient and safer maritime activities.
Q3: What are the challenges associated with implementing digitalization in the maritime sector?
Ans. Some challenges associated with implementing digitalization in the maritime sector include the high cost of technology adoption, cybersecurity concerns, data privacy issues, and the need for workforce training and upskilling to adapt to new technologies.
Q4: How is digitalization transforming traditional business models in the maritime industry?
Ans. Digitization is transforming traditional business models in the maritime industry by enabling new ways of working, such as remote monitoring and predictive maintenance. It is also creating new revenue streams through data-driven services and improving customer experiences.
Q5: What role do autonomous marine vehicles play in the future of maritime digitalization?
Ans. Autonomous marine vehicles, including autonomous ships and drones, are expected to play a significant role in the future of maritime digitalization. These vehicles can operate without human intervention, leading to increased efficiency, reduced costs, and improved safety in maritime operations.
Disclaimer :- The opinions expressed in this article belong solely to the author and may not necessarily reflect those of Merchant Navy Decoded. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information provided and disclaim any responsibility for it. Data and visuals used are sourced from publicly available information and may not be authenticated by any regulatory body. Reviews and comments appearing on our blogs represent the opinions of individuals and do not necessarily reflect the views of Merchant Navy Decoded. We are not responsible for any loss or damage resulting from reliance on these reviews or comments.
Reproduction, copying, sharing, or use of the article or images in any form is strictly prohibited without prior permission from both the author and Merchant Navy Decoded.




